As we head into the top of the 12 months, we see that 2024 turned out to be a fairly good 12 months for a lot of economies, particularly the U.S.
Recessions had been principally averted, inflation returned to round 2% and labor markets remained robust however now not strained. You could possibly say that this 12 months will finish with economies in a little bit of a “Goldilocks” state – not too sizzling, not too chilly.
Labor markets have softened however are nonetheless typically wholesome
One place the place that’s evident is in labor markets.
The previous 4 years have seen extremes for labor markets – from massive spikes in unemployment in the course of the early a part of Covid then to traditionally tight labor markets as economies reopened, resulting in a scarcity of staff.
Now, unemployment is usually close to traditionally low ranges, however in lots of international locations, it’s rising (chart beneath). That’s an indication that the availability of labor is again in keeping with demand for labor. In reality, within the U.S., the variety of jobs per particular person in search of work has fallen from 2-to-1 to a way more balanced 1.1-to-1.
That’s good for firms, because it’s getting simpler to rent workers. It’s additionally excellent news for inflation, because the tempo of wages progress can be slowing.
Jobs markets are “not too sizzling, and never too chilly.”
Chart 1: Unemployment charges are low (however principally rising)

Inflation is again close to 2% targets around the globe
Everyone knows that inflation elevated dramatically throughout Covid. That was principally on account of provide chain disruptions attributable to Covid, wage pressures from tight labor markets and the Ukraine battle. The costs of products, vitality and meals all rose. Information reveals that client costs within the U.S. are actually round 22% larger and wages are 25% larger than earlier than Covid.
However with provide chains fastened and wage progress cooling, headline inflation around the globe has fallen. It’s again round 2% in most of the world’s largest economies (chart beneath).
Briefly, inflation could be very near being “excellent.”
Chart 2: Inflation again close to central financial institution targets

GDP progress simply robust sufficient to keep away from recession
The primary software central banks used to get inflation again underneath management was larger rates of interest. Usually, that slows the financial system an excessive amount of, resulting in a recession, which many had been fearful about again in 2023.
Nevertheless, the information reveals that, though progress is gradual in some locations, most international locations have averted recession. Usually, international locations appear to have achieved a so-called “delicate touchdown.”
Chart 3: U.S. stands out for its robust progress amongst superior economies in 2024
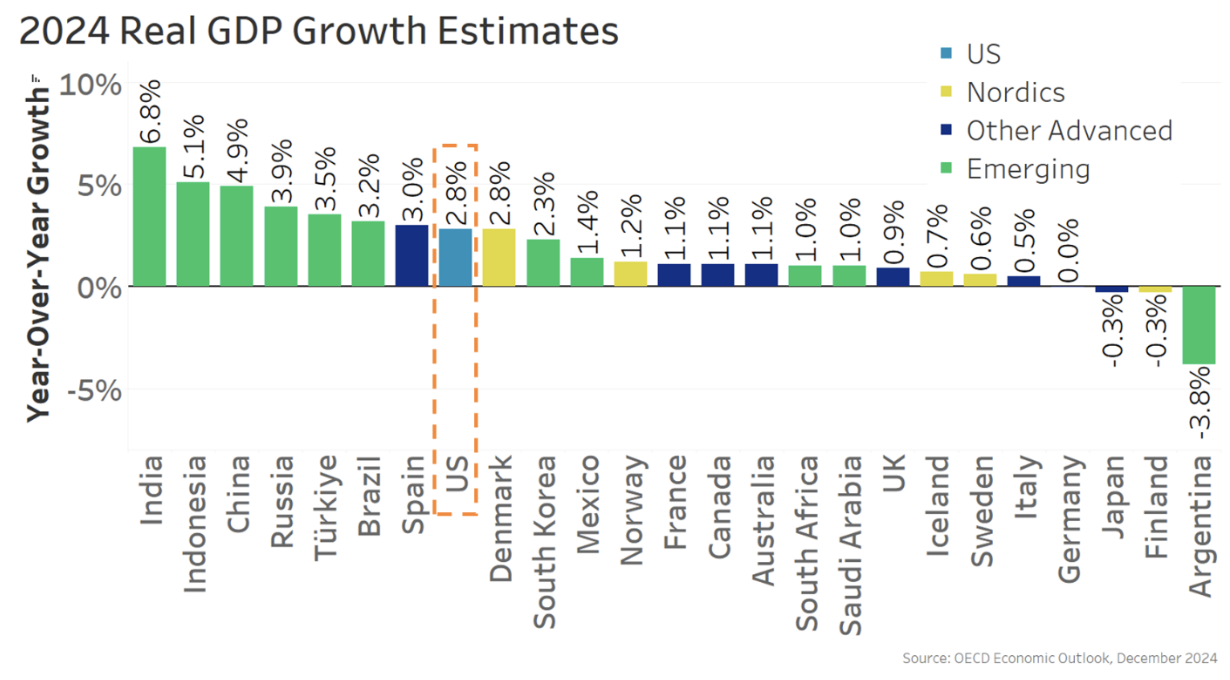
So, as we exit 2024, we’ve what’s fairly near a “Goldilocks” financial system – not too sizzling, not too chilly.
Curiously, the U.S. has seen one of many strongest economies in 2024, the place we’ve a 4.2% unemployment fee, 2.4% inflation fee, and are on tempo for practically 3% actual GDP progress.
Price cuts underway, with extra anticipated in 2025, ought to assist enhance progress
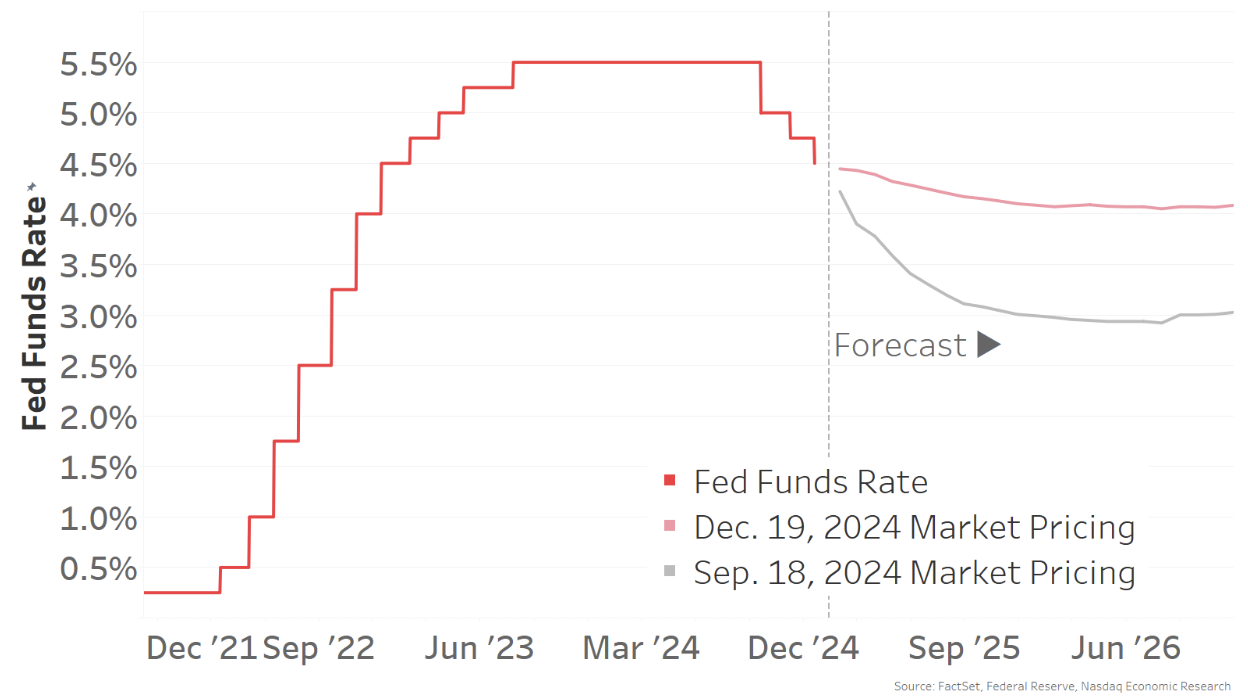
With inflation down and employment markets softer, central banks have already began to scale back charges. Based mostly on the U.S. Fed’s personal estimates, present short-term rates of interest are nonetheless at ranges which might be “restrictive” – or above the impartial fee. In consequence, charges are anticipated to fall extra in 2025. The massive query is how a lot.
Simply three months in the past, markets had been pricing in a Fed funds fee of round 3.0% by the top of 2025 – a fall of round 1.5% from present ranges.
By December, lots had modified. Markets now solely anticipate charges to fall to round 4.0%, and possibly not attain that degree till 2026. Briefly, we’re seeing charges staying higher-for-longer once more. For curiosity rate-sensitive segments of the financial system, that might have an effect on funding and progress.
Chart 4: Rates of interest are falling in most international locations, with extra cuts anticipated in 2025
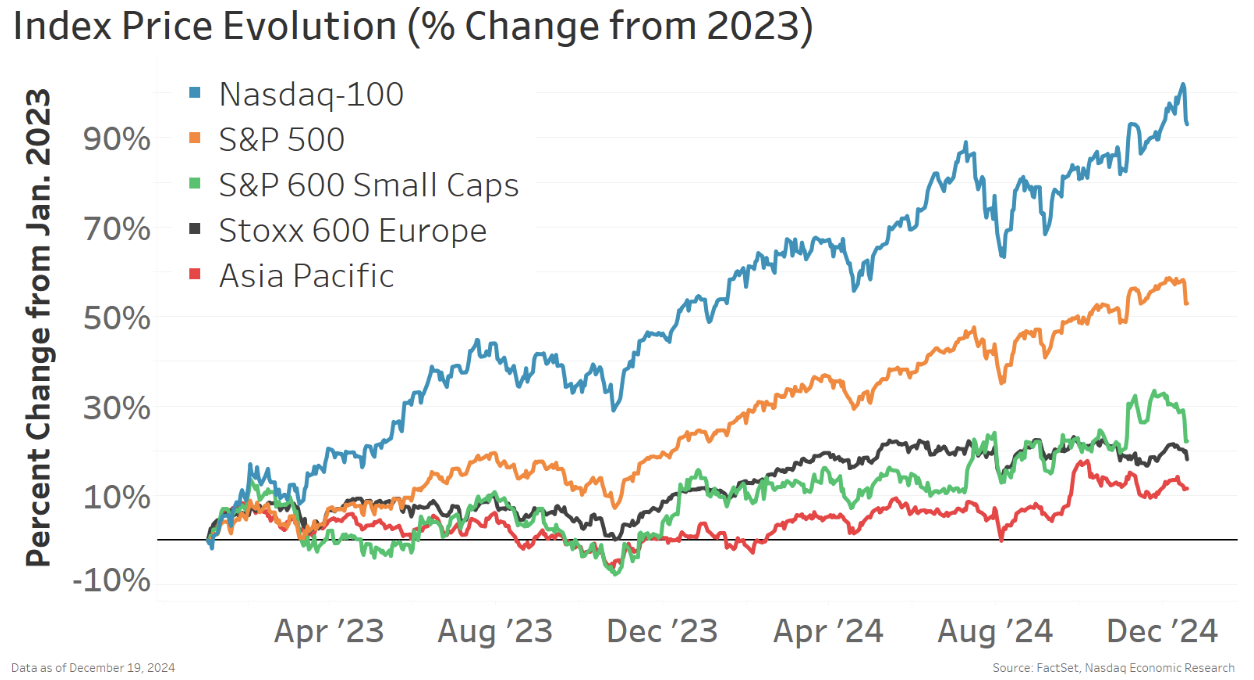
World inventory markets had a principally good 12 months in 2024
General, 2024 was a superb 12 months for inventory markets. Many international locations noticed earnings recoveries, which, mixed with decrease rates of interest, helped push inventory valuations up.
Nevertheless, returns within the U.S. massive cap shares – and particularly for Nasdaq-100® shares – had been a lot larger than most different areas or market caps.
Chart 5: Most inventory markets are up in 2024, however U.S. mega cap noticed stronger returns
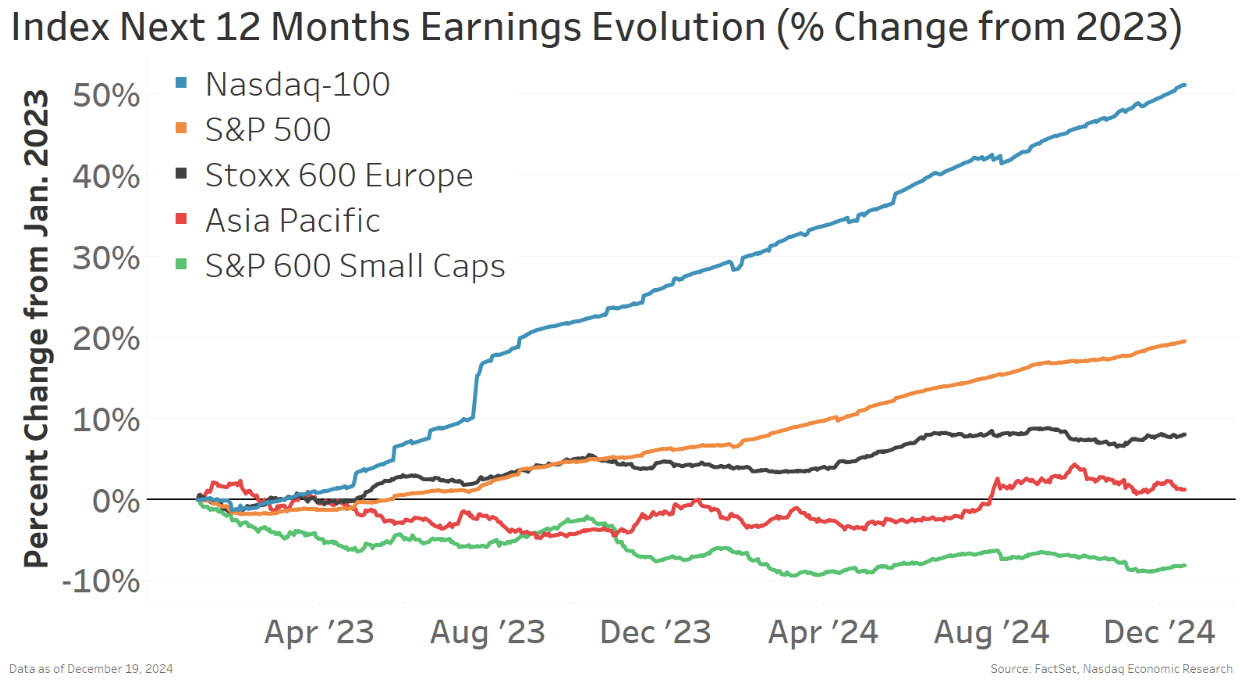
Curiously, earnings in the identical indexes we see the identical tendencies.
The outperformance of the Nasdaq-100® is supported by far stronger earnings progress. Whereas U.S. small caps are mired in an earnings recession.
Chart 6: Earnings tendencies mirror inventory returns
Taking a better have a look at earnings within the massive cap indexes, we see that earnings progress within the S&P 500 has been pushed predominantly by the so referred to as “Magazine 7” shares.
All these shares are uncovered to the spending on synthetic intelligence, which some estimate is operating nicely over $200 billion per 12 months. Nvidia makes the GPU chips wanted for calibrating AI fashions. Amazon, Microsoft and Google all run cloud information facilities, that are key to processing all the information, and Apple, Tesla and Meta are among the many first movers utilizing AI of their merchandise.
As a result of all are Nasdaq listings, they make up a fair bigger proportion of the Nasdaq-100 Index® – serving to the Nasdaq-100® outperform the broader S&P 500 index.
Chart 7: Giant-cap earnings are pushed by the Magazine 7 shares
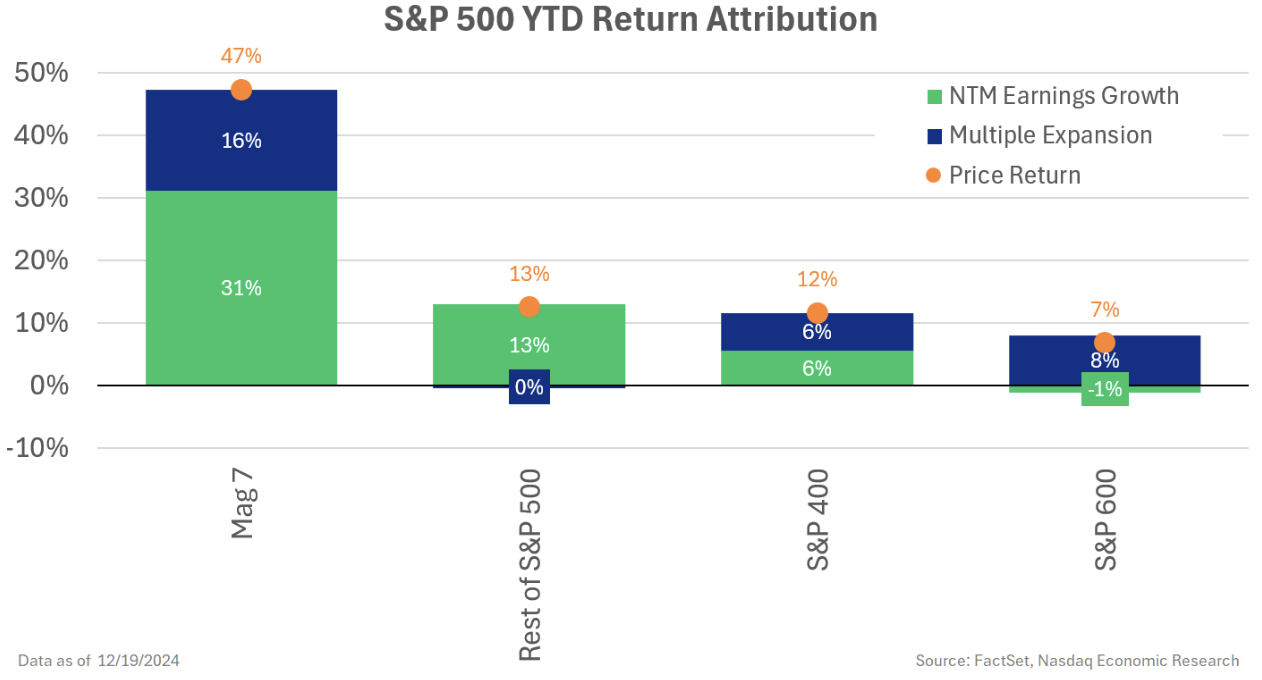
Importantly although, as we’ve progressed via 2024, we’ve seen a broadening of the earnings restoration in the remainder of the big cap shares.
Decrease charges can be good for small firms
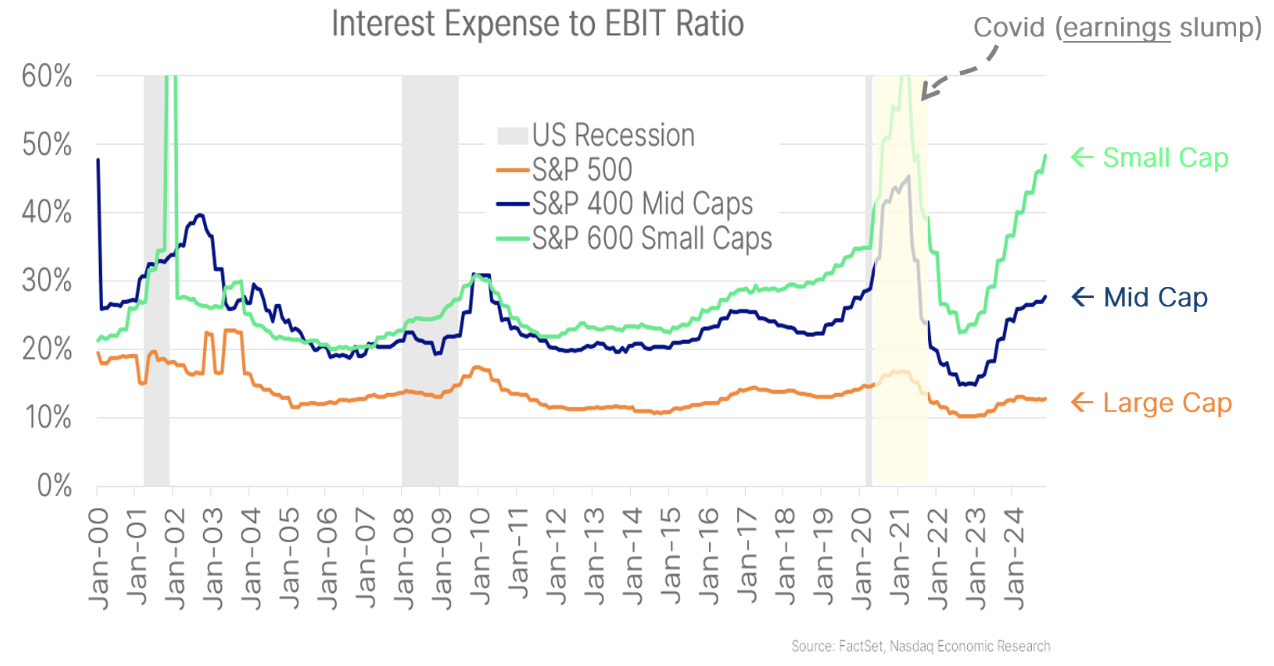
Once we have a look at the distinction between large-cap and small-cap shares, one factor stands out. Curiosity bills are decreasing earnings of small cap firms far more than for large-cap firms.
Some information reveals that larger rates of interest have particularly impacted smaller firms, with curiosity expense/revenue ratios at multidecade excessive ranges. In distinction, the proportion of curiosity expense for giant cap firms is close to file low ranges – and has hardly elevated regardless of rising rates of interest.
Chart 8: Rates of interest are affecting small-cap firms far more than bigger firms
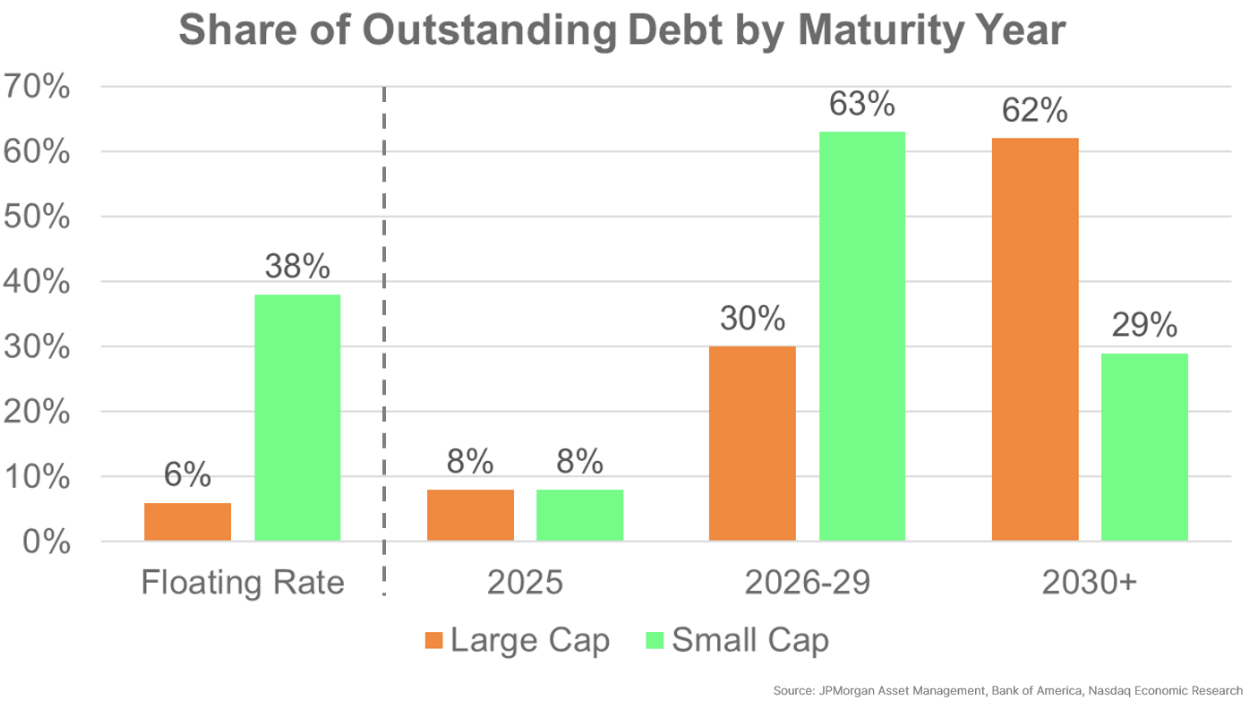
The totally different sensitivity to rates of interest is supported by firm debt financing throughout market cap. We see that large-cap firms have little or no floating fee debt, which has insulated them from Fed rate of interest will increase. In reality, large-cap firms appear to have fastened charges on nearly all of their debt, at low charges, out to no less than 2030.
In distinction, small-cap firms have round a 3rd of their debt at floating charges, with a big proportion of fastened fee debt scheduled to refinance beginning in 2026. Clearly, small-cap firms will probably be extra impacted by charges staying higher-for-longer.
Chart 9: Small-cap firms are far more uncovered to larger short-term rates of interest
2025: No indicators but of client weak spot
General, the explanation the U.S. financial system carried out so nicely in 2024 was as a result of the U.S. client remained robust. Actual spending (adjusted for inflation) is up virtually 15% in comparison with proper earlier than Covid. That’s lots higher than Europe, the place actual spending has barely elevated.
Chart 10: U.S. client spending stands out amongst different superior economies

A variety of components have helped keep client spending progress within the U.S.
Firstly, after experiencing the Credit score Disaster again in 2008, most U.S. households have now locked in long-term fastened mortgage charges. Similar to large-cap firms, regardless of the Fed rising official rates of interest and new mortgage charges virtually tripling, the typical rate of interest on excellent mortgages barely elevated – and stays round 4%. That has left extra money in folks’s pockets – and means financial coverage has had a extra muted affect on customers.
Secondly, with wage features that began within the “Nice Resignation,” after which broadened to incorporate most staff, actual wages have additionally grown. That, mixed with robust employment and low dangers of layoffs, has given the patron the arrogance to maintain spending.
With rates of interest larger, even savers are incomes extra revenue.
Lastly, larger home costs have additionally left family steadiness sheets in a robust place. Latest information displaying will increase in house fairness loans (HELOCs) counsel some may lastly be tapping into debt markets, permitting spending to persist.
To this point, there are few indicators of weak spot. Bank card debt, though at new highs, is comparatively low as a proportion of revenue and family internet belongings. In reality, even the rise in unemployment (Chart 1) that the U.S. has seen is usually on account of extra staff in search of jobs. Layoffs, which extra usually lead into recessions, stay close to multidecade low ranges.
Chart 11: Low layoffs have helped customers hold spending

2025: Sturdy underlying financial system with an opportunity of uncertainty
There are plenty of constructive indicators for the U.S. financial system and the inventory market heading into 2025.
The patron stays robust, because of sturdy family steadiness sheets and a robust job market.
Firm earnings are recovering. Anticipated tax cuts and looser regulation in 2025 ought to assist enhance earnings, too. Though some uncertainty exists for firms that need to take care of larger longer-term rates of interest, doable new tariffs and potential new labor shortages.
Trying on the greater image, additional rate of interest cuts, mixed with tax cuts and internet constructive authorities spending, ought to hold the U.S. financial system rising for no less than one other 12 months. That also needs to be good for shares.
As we head into the top of the 12 months, we see that 2024 turned out to be a fairly good 12 months for a lot of economies, particularly the U.S.
Recessions had been principally averted, inflation returned to round 2% and labor markets remained robust however now not strained. You could possibly say that this 12 months will finish with economies in a little bit of a “Goldilocks” state – not too sizzling, not too chilly.
Labor markets have softened however are nonetheless typically wholesome
One place the place that’s evident is in labor markets.
The previous 4 years have seen extremes for labor markets – from massive spikes in unemployment in the course of the early a part of Covid then to traditionally tight labor markets as economies reopened, resulting in a scarcity of staff.
Now, unemployment is usually close to traditionally low ranges, however in lots of international locations, it’s rising (chart beneath). That’s an indication that the availability of labor is again in keeping with demand for labor. In reality, within the U.S., the variety of jobs per particular person in search of work has fallen from 2-to-1 to a way more balanced 1.1-to-1.
That’s good for firms, because it’s getting simpler to rent workers. It’s additionally excellent news for inflation, because the tempo of wages progress can be slowing.
Jobs markets are “not too sizzling, and never too chilly.”
Chart 1: Unemployment charges are low (however principally rising)

Inflation is again close to 2% targets around the globe
Everyone knows that inflation elevated dramatically throughout Covid. That was principally on account of provide chain disruptions attributable to Covid, wage pressures from tight labor markets and the Ukraine battle. The costs of products, vitality and meals all rose. Information reveals that client costs within the U.S. are actually round 22% larger and wages are 25% larger than earlier than Covid.
However with provide chains fastened and wage progress cooling, headline inflation around the globe has fallen. It’s again round 2% in most of the world’s largest economies (chart beneath).
Briefly, inflation could be very near being “excellent.”
Chart 2: Inflation again close to central financial institution targets

GDP progress simply robust sufficient to keep away from recession
The primary software central banks used to get inflation again underneath management was larger rates of interest. Usually, that slows the financial system an excessive amount of, resulting in a recession, which many had been fearful about again in 2023.
Nevertheless, the information reveals that, though progress is gradual in some locations, most international locations have averted recession. Usually, international locations appear to have achieved a so-called “delicate touchdown.”
Chart 3: U.S. stands out for its robust progress amongst superior economies in 2024

So, as we exit 2024, we’ve what’s fairly near a “Goldilocks” financial system – not too sizzling, not too chilly.
Curiously, the U.S. has seen one of many strongest economies in 2024, the place we’ve a 4.2% unemployment fee, 2.4% inflation fee, and are on tempo for practically 3% actual GDP progress.
Price cuts underway, with extra anticipated in 2025, ought to assist enhance progress
With inflation down and employment markets softer, central banks have already began to scale back charges. Based mostly on the U.S. Fed’s personal estimates, present short-term rates of interest are nonetheless at ranges which might be “restrictive” – or above the impartial fee. In consequence, charges are anticipated to fall extra in 2025. The massive query is how a lot.
Simply three months in the past, markets had been pricing in a Fed funds fee of round 3.0% by the top of 2025 – a fall of round 1.5% from present ranges.
By December, lots had modified. Markets now solely anticipate charges to fall to round 4.0%, and possibly not attain that degree till 2026. Briefly, we’re seeing charges staying higher-for-longer once more. For curiosity rate-sensitive segments of the financial system, that might have an effect on funding and progress.
Chart 4: Rates of interest are falling in most international locations, with extra cuts anticipated in 2025

World inventory markets had a principally good 12 months in 2024
General, 2024 was a superb 12 months for inventory markets. Many international locations noticed earnings recoveries, which, mixed with decrease rates of interest, helped push inventory valuations up.
Nevertheless, returns within the U.S. massive cap shares – and particularly for Nasdaq-100® shares – had been a lot larger than most different areas or market caps.
Chart 5: Most inventory markets are up in 2024, however U.S. mega cap noticed stronger returns

Curiously, earnings in the identical indexes we see the identical tendencies.
The outperformance of the Nasdaq-100® is supported by far stronger earnings progress. Whereas U.S. small caps are mired in an earnings recession.
Chart 6: Earnings tendencies mirror inventory returns

Taking a better have a look at earnings within the massive cap indexes, we see that earnings progress within the S&P 500 has been pushed predominantly by the so referred to as “Magazine 7” shares.
All these shares are uncovered to the spending on synthetic intelligence, which some estimate is operating nicely over $200 billion per 12 months. Nvidia makes the GPU chips wanted for calibrating AI fashions. Amazon, Microsoft and Google all run cloud information facilities, that are key to processing all the information, and Apple, Tesla and Meta are among the many first movers utilizing AI of their merchandise.
As a result of all are Nasdaq listings, they make up a fair bigger proportion of the Nasdaq-100 Index® – serving to the Nasdaq-100® outperform the broader S&P 500 index.
Chart 7: Giant-cap earnings are pushed by the Magazine 7 shares

Importantly although, as we’ve progressed via 2024, we’ve seen a broadening of the earnings restoration in the remainder of the big cap shares.
Decrease charges can be good for small firms
Once we have a look at the distinction between large-cap and small-cap shares, one factor stands out. Curiosity bills are decreasing earnings of small cap firms far more than for large-cap firms.
Some information reveals that larger rates of interest have particularly impacted smaller firms, with curiosity expense/revenue ratios at multidecade excessive ranges. In distinction, the proportion of curiosity expense for giant cap firms is close to file low ranges – and has hardly elevated regardless of rising rates of interest.
Chart 8: Rates of interest are affecting small-cap firms far more than bigger firms

The totally different sensitivity to rates of interest is supported by firm debt financing throughout market cap. We see that large-cap firms have little or no floating fee debt, which has insulated them from Fed rate of interest will increase. In reality, large-cap firms appear to have fastened charges on nearly all of their debt, at low charges, out to no less than 2030.
In distinction, small-cap firms have round a 3rd of their debt at floating charges, with a big proportion of fastened fee debt scheduled to refinance beginning in 2026. Clearly, small-cap firms will probably be extra impacted by charges staying higher-for-longer.
Chart 9: Small-cap firms are far more uncovered to larger short-term rates of interest

2025: No indicators but of client weak spot
General, the explanation the U.S. financial system carried out so nicely in 2024 was as a result of the U.S. client remained robust. Actual spending (adjusted for inflation) is up virtually 15% in comparison with proper earlier than Covid. That’s lots higher than Europe, the place actual spending has barely elevated.
Chart 10: U.S. client spending stands out amongst different superior economies

A variety of components have helped keep client spending progress within the U.S.
Firstly, after experiencing the Credit score Disaster again in 2008, most U.S. households have now locked in long-term fastened mortgage charges. Similar to large-cap firms, regardless of the Fed rising official rates of interest and new mortgage charges virtually tripling, the typical rate of interest on excellent mortgages barely elevated – and stays round 4%. That has left extra money in folks’s pockets – and means financial coverage has had a extra muted affect on customers.
Secondly, with wage features that began within the “Nice Resignation,” after which broadened to incorporate most staff, actual wages have additionally grown. That, mixed with robust employment and low dangers of layoffs, has given the patron the arrogance to maintain spending.
With rates of interest larger, even savers are incomes extra revenue.
Lastly, larger home costs have additionally left family steadiness sheets in a robust place. Latest information displaying will increase in house fairness loans (HELOCs) counsel some may lastly be tapping into debt markets, permitting spending to persist.
To this point, there are few indicators of weak spot. Bank card debt, though at new highs, is comparatively low as a proportion of revenue and family internet belongings. In reality, even the rise in unemployment (Chart 1) that the U.S. has seen is usually on account of extra staff in search of jobs. Layoffs, which extra usually lead into recessions, stay close to multidecade low ranges.
Chart 11: Low layoffs have helped customers hold spending

2025: Sturdy underlying financial system with an opportunity of uncertainty
There are plenty of constructive indicators for the U.S. financial system and the inventory market heading into 2025.
The patron stays robust, because of sturdy family steadiness sheets and a robust job market.
Firm earnings are recovering. Anticipated tax cuts and looser regulation in 2025 ought to assist enhance earnings, too. Though some uncertainty exists for firms that need to take care of larger longer-term rates of interest, doable new tariffs and potential new labor shortages.
Trying on the greater image, additional rate of interest cuts, mixed with tax cuts and internet constructive authorities spending, ought to hold the U.S. financial system rising for no less than one other 12 months. That also needs to be good for shares.










